Osteochondrosis is a disease of the skeletal system, characterized by changes in cartilage tissue. As a result of the development of the disease, a person's working ability decreases, blood circulation and the integrity of the vertebral disc are disturbed. Often, the disease develops due to obesity, physical inactivity, frequent spending on computers or driving a car.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as it develops, is characterized by the following symptoms:
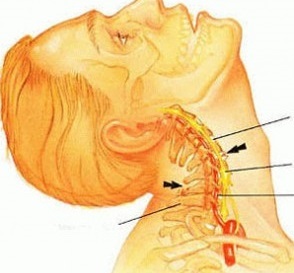
Neck pain with cervical osteochondrosis
- Persistent headache. Patients with osteochondrosis mainly experience headaches, which are exacerbated by sharp neck turns or sudden head movements.
- Neck pain that may radiate to the shoulder area. It usually appears in the morning, immediately after sleep, decreases or disappears completely after warming up the neck muscles.
- Cervical lumbago, characterized by sharp pain in the neck, hardening of the muscles in the affected area and limited movement.
- Pain in the sternum or gallbladder. Patients most often suspect they have pathology of the cardiovascular system, but taking nitroglycerin does not relieve pain. When cervical osteochondrosis is indicated by pain in the sternum, the patient complains of a decrease in muscle strength in the arm.
- In almost all patients with osteochondrosis, you may hear features and cracks if you ask someone to tilt their head in different directions.
- A hoarse voice.
- Osteochondrosis of the neck can be manifested by numbness in the tongue, fingertips (symptoms occur due to compression of nerves and ducts located next to the intervertebral disc.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Limb paresis, decreased muscle strength in the limbs.
The cause of the above symptoms is damage to the connective tissue and intervertebral disc with its subsequent deformation. As a result of pathological processes, the disc becomes overgrown with bone formation, osteophytes form, which squeeze and damage blood vessels and nerve vessels.
Level of disease
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine develops in several stages. The more the patient's disease develops, the more symptoms, the more serious the complications of the disease.
Grade 1 cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by damage to the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc. When metabolism is disrupted in the body, the nucleus pulposus, which is the structure of biopolymer compounds, is destroyed. Initially, it loses water, gradually dries out, and its size decreases. Its strength decreases significantly and it becomes more difficult for the spine to cope with physical activity. At this stage of the disease, a person does not feel sick, does not seek medical help. If you begin to identify osteochondrosis at this stage, then the patient will not need medication treatment.
Grade 2 cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by damage to the annulus fibrosus in the intervertebral disc. Cracks and tears appear on the surface of the disc due to the strong and uneven load on the spine. Due to the fact that the annulus fibrosus becomes thinner, the nucleus is actually squeezed into tears and the resulting cracks, thus expanding. As a result, the disc enlarges, beginning to protrude beyond the edges of the vertebrae. This phenomenon is called disc protrusion. Stage 2 cervical osteochondrosis is the stage of the disease in which a person first feels pain.
Grade 3 cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by the formation of a hernia. The fibrosus annulus not only becomes thinner, but ruptures, so the nucleus pulposus "flows" into the subglotic space, forming a herniated disc. As a result of the development of the process, all the surrounding tissues suffer - ligaments and muscles, nerves and blood vessels.
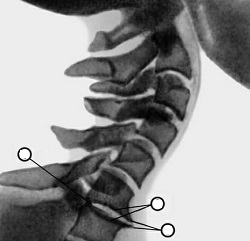
Over time, the vertebral skeletal system changes: the edges of the vertebrae change shape, become ribbed and even sharp. The muscles around the altered bone system contract inadvertently, thus restricting the movement of the spine. All nerve fibers that travel through the spinal cord are disrupted, the flow of nerve impulses from the brain to organs and tissues is disrupted. It is important that the symptoms of osteochondrosis appear depending on the location of osteochondrosis.
Grade 4 cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by degenerative reconstruction of the spine. After the destructive process in the body, the recovery process begins. The duration of the fourth stage is about one year. During this time, the nature of bone growth in the deformed vertebrae changed. The bones begin to grow wide, causing the vertebral area to increase. Such medicinal growths are called osteophytes. Thanks to them, the movement of the injured spine is reduced, and the process of its destruction is delayed. Over time, the fully inactive vertebra becomes a static bone column.
And if the pain syndrome decreases, the pinched nerves and blood vessels remain in place, they are not only squeezed by the discs and spine, but also by the osteophytes that form. Such a process must be properly treated to prevent the consequences of the disease.
Complications of cervical osteochondrosis
The main consequences of the development of cervical osteochondrosis are:
- Vascular disorders (arterial compression);
- Formation of hernias with varying degrees of severity;
- Spinal cord injury;
- Osteophyte formation;
- Limited mobility of the spine.
What are the possible complications of cervical osteochondrosis osteochondrosis? The most dangerous consequence is the deterioration of blood supply to the brain. As a result of arterial compression, less blood enters the brain, and gray matter is less supplied with oxygen.
If the patient has vertebral artery syndrome - when the main bloodstream to the brain is pinched, then the person experiences dizziness, fainting.
In addition to impaired consciousness, patients with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine experience visual and hearing impairments. In addition to numbness in the limbs, it is possible to develop Dupuytren syndrome, which is characterized by hand cramps. As a result of the development of the syndrome, finger movement is lost.
Hypertension and vegetative-vascular dystonia (VVD) are considered frequent complications. The cosmetic defect that arises as a result of the development of osteochondrosis is the formation of withers ("mounds" of cartilage tissue in the back of the head).
Methods of treatment
Treatment options for cervical osteochondrosis depend on the stage of the disease. Medical treatment consists of prescribing non-steroidal analgesic, analgesic and antispasmodic drugsThe dose of the drug is adjusted at the discretion of the doctor.
Physical therapy is often prescribed to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae. With the help of exercise, you can not only relieve pain, but also reduce inflammation, strengthen the back muscles, and reduce the risk of complications.
Massage has a general strengthening effect. After a massage, patients with osteochondrosis will lose tension and pain, and blood supply will increase.
When medication does not help, the doctor should prescribe surgery. During surgery, the doctor removes the part of the intervertebral disc that compresses the nerve root.
The best treatment is a combination of several methods. Medical treatment must be combined with massage, physiotherapy and gymnastics training.
Some doctors believe that acupuncture and herbal medicine are effective treatment methods.
Prevention
To reduce pain and prevent the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, you can use a simple method. For starters, everyone should always be in a position that relieves the load on the spine. Keep in mind about exercises that knead muscles and support metabolic processes in the spine. To get a positive result, you must follow the recommendations given by the doctor.
Key Suggestions:
- Spread physical activity evenly throughout the spinal space. To do this, limit vertical loads, avoid sudden movements and exercises that can damage the spine. Falling or jumping from high altitudes should be avoided.
- Do not carry heavy objects with outstretched arms. Before taking an object off the floor, you can not bend forward, but bend down.
- Do not move objects with one hand, it is recommended to distribute the load on both limbs. If this is not possible, you should place the load in a suitcase on wheels or a backpack.
- If you need to carry a heavy load, you should wear a wide belt or buy a special corset before work.
- Wear comfortable shoes.
- The best disease prevention is swimming, regular gymnastics, bathing in contrast.
- Stressful situations should be avoided.
- You have to remember the rules of a balanced diet.
- Get rid of bad habits.
It should be understood that it is much easier to prevent a disease than to cure it in a long and continuous period. If surgery is not necessary in the early stages of the disease, then the next stage of osteochondrosis requires surgical intervention.

















































